1. React 介绍

React 是一个用于构建用户界面的 JavaScript 库,它只负责应用的视图层,帮助开发人员构建快速且交互式的 web 应用程序。
React 使用组件的方式构建用户界面。
2. JSX 语法
在 React 中使用 JSX 语法描述用户界面,它是一种 JavaScript 语法扩展。
在 React 代码执行之前,Babel 会将 JSX 语法转换为标准的 JavaScript API。
JSX 语法就是一种语法糖,让开发人员使用更加舒服的代码构建用户界面。
2.1 在 JSX 中使用表达式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| const user = {
firstName: 'Harper',
lastName: 'Perez'
}
function formatName(user) {
return user.firstName + ' ' + user.lastName;
}
const element = <h1>Hello, {formatName(user)}!</h1>;
|
JSX 本身其实也是一种表达式,将它赋值给变量,当作参数传入,作为返回值都可以。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| function getGreeting(user) {
if (user) {
return <h1>Hello, {formatName(user)}!</h1>;
}
return <h1>Hello, Stranger.</h1>;
}
|
2.2 属性
如果属性值为字符串类型,需要加引号,属性名称推荐采用驼峰式命名法。
1
| const element = <div greeting="hello"></div>;
|
如果属性值为 JavaScript 表达式,属性值外面加大括号。
1
2
| const element = <img src={user.avatarUrl} />;
// 注意大括号外面不能加引号,JSX 会将引号当中的内容识别为字符串而不是表达式
|
2.3 JSX 单标记必须闭合
如果 JSX 是单标记,必须闭合,否则报错。
1
2
| const element = <img src={user.avatarUrl} />
const element = <input type="text"/>
|
2.4 className
为 JSX 标记添加类名需要使用 className,而不是 class。
1
| const element = <img src={user.avatarUrl} className="rounded"/>;
|
2.5 JSX 自动展开数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| const ary = [<p>哈哈</p>, <p>呵呵</p>, <p>嘿嘿</p>];
const element = (
<div>{ary}</div>
);
// 解析后
/*
<div>
<p>哈哈</p>
<p>呵呵</p>
<p>嘿嘿</p>
</div>
*/
|
2.6 三元运算
1
2
| { boolean ? <div>Hello React</div> : null }
{ boolean && <div>Hello React</div> }
|
2.7 循环
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| const persons = [{
id: 1,
name: '张三',
age: 20
}, {
id: 2,
name: '李四',
age: 15
}, {
id: 3,
name: '王五',
age: 22
}]
|
1
2
3
| <ul>
{ persons.map(person => <li key={person.id}> {person.name} {person.age} </li>) }
</ul>
|
2.8 事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
| {/* 第一个参数即是事件对象 不需传递 */}
<button onClick={this.eventHandler}>按钮</button>
{/* 需要传递事件对象 */}
<button onClick={e=>this.eventHandler('arg',e)}>按钮</button>
{/* 最后一个参数即是事件对象 不需传递 */}
<button onClick={this.eventHandler.bind(null, 'arg')}>按钮</button>
|
1
2
3
4
5
| constructor () {
this.eventHandler = this.eventHandler.bind(this)
}
eventHandler () {}
<button onClick={this.eventHandler}>按钮</button>
|
2.9 样式
2.9.1 行内样式
1
2
3
4
5
6
| class App extends Component {
render() {
const style = {width: 200, height: 200, backgroundColor: 'red'};
return <div style={style}></div>
}
}
|
2.9.2 外链样式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| // Button.js
import styles from './Button.module.css';
class Button extends Component {
render() {
return <button className={styles.error}>Error Button</button>;
}
}
|
2.9.3 全局样式
2.10 ref 属性
2.10.1 createRef
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| class Input extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.inputRef = React.createRef()
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref={this.inputRef} />
<button onClick={() => console.log(this.inputRef.current)}> button </button>
</div>
)
}
}
|
2.10.2 函数参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| class Input extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref={input => (this.input = input)} />
<button onClick={() => console.log(this.input)}>button</button>
</div>
)
}
}
|
2.10.3 ref 字符串
不推荐使用,在严格模式下报错。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| class Input extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref="username" />
<button onClick={() => console.log(this.refs.username)}>button</button>
</div>
)
}
}
|
2.10.4 获取组件实例
点击按钮让 input 文本框获取焦点。
input 文本框以及让文本框获取焦点的方法定义在 Input 组件中,在 App 组件中引入 Input 组件,按钮定义在 App 组件中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| // Input.js
class Input extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.inputRef = React.createRef()
this.focusInput = this.focusInput.bind(this)
}
focusInput() {
this.inputRef.current.focus()
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref={this.inputRef} />
</div>
)
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| // App.js
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.InputComponentRef = React.createRef()
}
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<Input ref={this.InputComponentRef} />
<button onClick={() => this.InputComponentRef.current.focusInput()}>button</button>
</div>
)
}
|

3. 组件
3.1 什么是组件
React 是基于组件的方式进行用户界面开发的. 组件可以理解为对页面中某一块区域的封装。
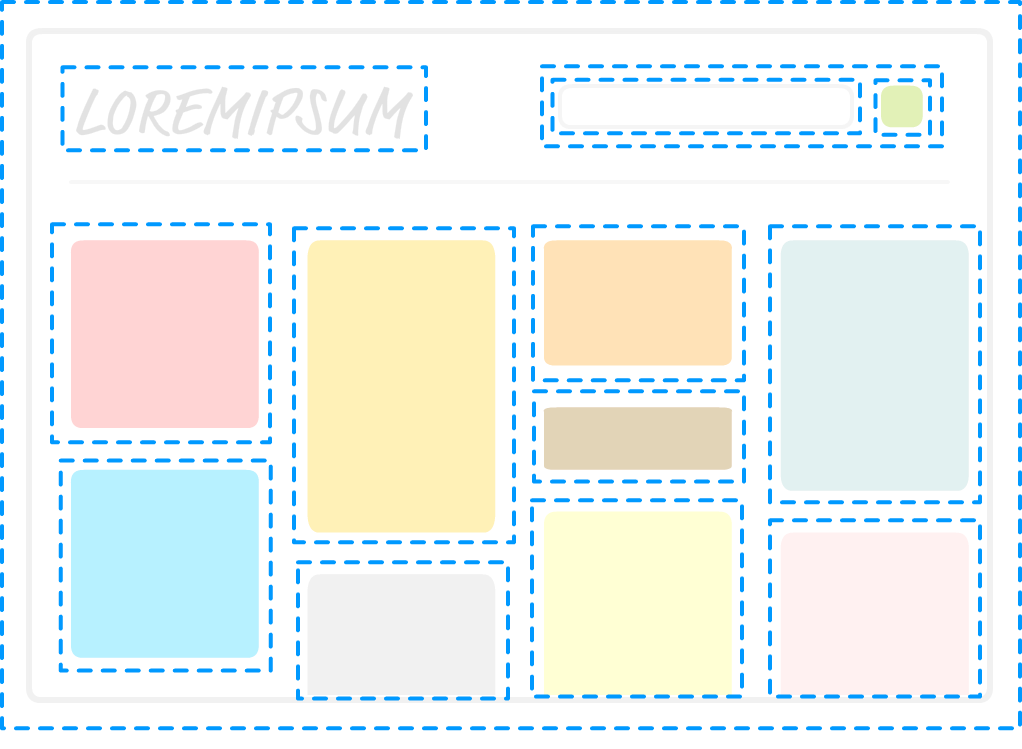
3.2 创建组件
3.2.1 创建类组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render () {
return <div>Hello, 我是类组件</div>
}
}
|
3.2.2 创建函数组件
1
2
3
| const Person = () => {
return <div>Hello, 我是函数型组件</div>;
}
|
注意事项
- 组件名称首字母必须大写,用以区分组件和普通标签。
- jsx 语法外层必须有一个根元素
3.3 组件 props
3.3.1 props 传递数据
在调用组件时可以向组件内部传递数据,在组件中可以通过 props 对象获取外部传递进来的数据。
1
2
| <Person name="乔治" age="20"/>
<Person name="玛丽" age="10"/>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| // 类组件
class Person extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h3>姓名:{this.props.name}</h3>
<h4>年龄:{this.props.age}</h4>
</div>
);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| // 函数组件
const Person = props => {
return (
<div>
<h3>姓名:{props.name}</h3>
<h4>年龄:{props.age}</h4>
</div>
);
}
|
注意:
- props 对象中存储的数据是只读的,不能在组件内部被修改。
- 当 props 数据源中的数据被修改后,组件中的接收到的 props 数据会被同步更新。( 数据驱动 DOM )
3.3.2 设置 props 默认值
1
2
3
| class App extends Component {
static defaultProps = {}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| function ThemedButton(props) {
}
ThemedButton.defaultProps = {
theme: "secondary",
label: "Button Text"
};
|
3.3.3 组件 children
通过 props.children 属性可以获取到在调用组件时填充到组件标签内部的内容。
1
| <Person>组件内部的内容</Person>
|
1
2
3
4
5
| const Person = (props) => {
return (
<div>{props.children}</div>
);
}
|
3.3.4 单向数据流
在 React 中, 关于数据流动有一条原则, 就是单向数据流动, 自顶向下, 从父组件到子组件.
单向数据流特性要求我们共享数据要放置在上层组件中.
子组件通过调用父组件传递过来的方法更改数据.
当数据发生更改时, React 会重新渲染组件树.
单向数据流使组件之间的数据流动变得可预测. 使得定位程序错误变得简单.
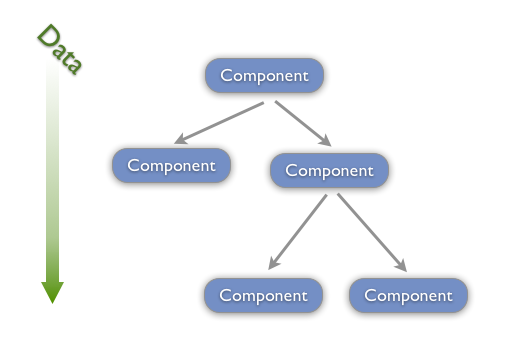
3.4 类组件状态 state
3.4.1 定义组件状态
类组件除了能够从外部 (props) 接收状态数据以外还可以拥有自己的状态 (state),此状态在组件内部可以被更新,状态更新 DOM 更新。
组件内部的状态数据被存储在组件类中的 state 属性中,state 属性值为对象类型,属性名称固定不可更改。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| class App extends Component {
constructor () {
super()
this.state = {
person: { name: '张三', age: 20 },
}
}
render () {
return (
<div>
{this.state.person.name}
{this.state.person.age}
</div>
);
}
}
|
3.4.2 更改组件状态
state 状态对象中的数据不可直接更改,如果直接更改 DOM 不会被更新,要更改 state 状态数据需要使用 setState 方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class App extends Component {
constructor () {
this.state = {
person: { name: '张三', age: 20 },
}
this.changePerson = this.changePerson.bind(this)
}
changePerson () {
this.setState({
person: {
name: '李四',
age: 15
}
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.state.person.name}
{this.state.person.age}
<button onClick={this.changePerson}>按钮</button>
</div>
);
}
}
|
3.4.3 双向数据绑定
双向数据绑定是指,组件类中更新了状态,DOM 状态同步更新,DOM 更改了状态,组件类中同步更新。组件 <=> 视图。
要实现双向数据绑定需要用到表单元素和 state 状态对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class App extends Component {
constructor () {
this.state = {
name: "张三"
}
this.nameChanged = this.nameChanged.bind(this)
}
nameChanged (event) {
this.setState({name: event.target.value});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>{this.state.name}</div>
<Person name={this.state.name} changed={this.nameChanged}/>
</div>
)
}
}
|
1
2
3
| const Person = props => {
return <input type="text" value={props.name} onChange={props.changed}/>;
}
|
3.5 类组件生命周期函数
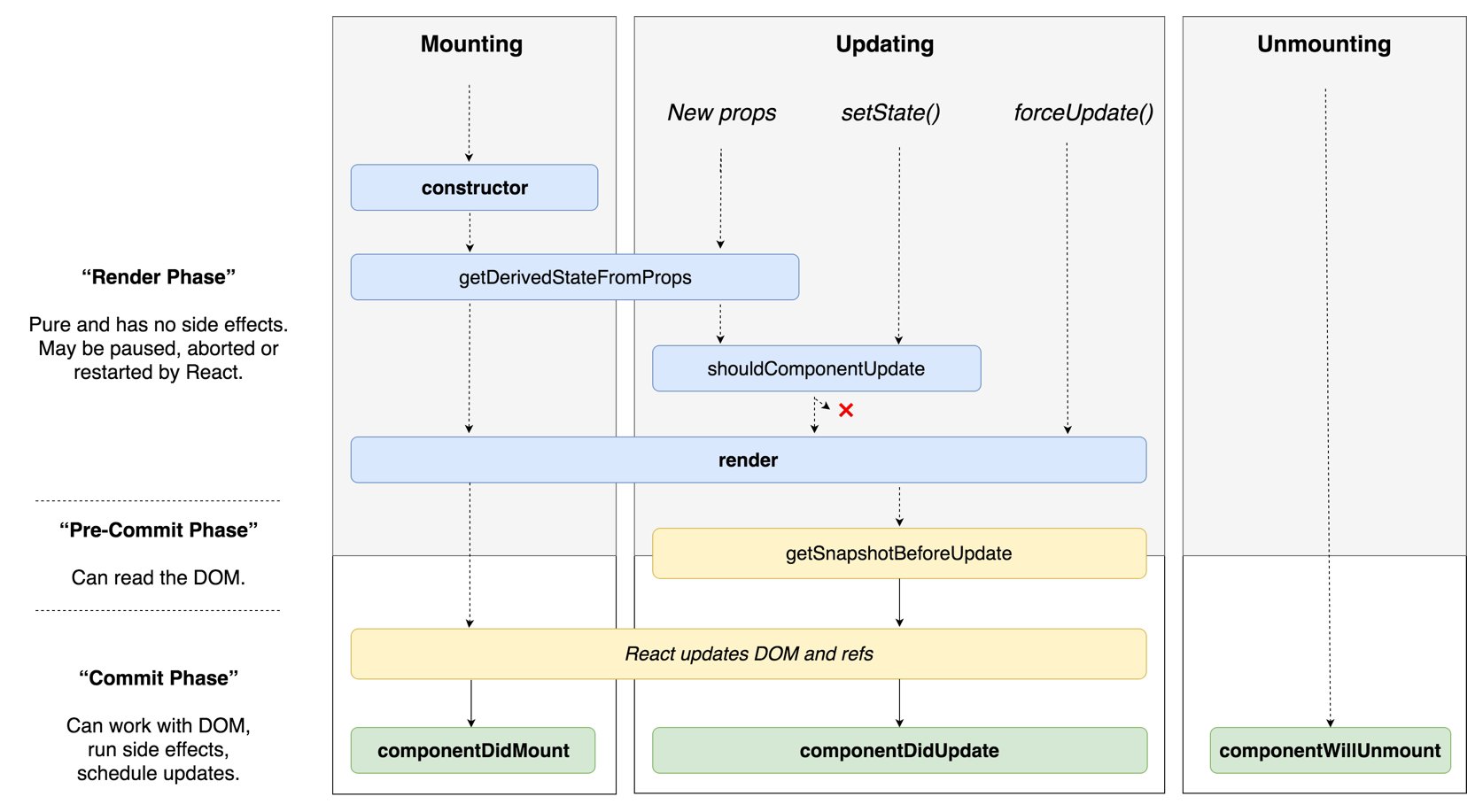
在组件完成更新之前需要做某种逻辑或者计算,就需要用到快照
1
| componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {}
|
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 方法会在组件完成更新之前执行,用于执行某种逻辑或计算,返回值可以在 componentDidUpdate 方法中的第三个参数中获取,就是说在组件更新之后可以拿到这个值再去做其他事情。
1
2
3
| getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
return 'snapshot'
}
|
3.6 Context
通过 Context 可以跨层级传递数据

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| // userContext.js
import React from "react"
const userContext = React.createContext("default value")
const UserProvider = userContext.Provider
const UserConsumer = userContext.Consumer
export { UserProvider, UserConsumer }
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| // App.js
import { UserProvider } from "./userContext"
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<UserProvider value="Hello React Context">
<A />
</UserProvider>
)
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| // C.js
import { UserConsumer } from "./userContext"
export class C extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<UserConsumer>
{username => {
return <div>{username}</div>
}}
</UserConsumer>
</div>
)
}
}
|
context 的另一种用法
1
2
| // userContext.js
export default userContext
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| // C.js
import userContext from "./userContext"
export class C extends Component {
static contextType = userContext
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.context}
</div>
)
}
}
|
4. 表单
4.1 受控表单
表单控件中的值由组件的 state 对象来管理,state 对象中存储的值和表单控件中的值时同步状态的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class App extends Component {
constructor () {
this.state = { username: "" }
this.nameChanged = this.nameChanged.bind(this)
}
nameChanged (e) {
this.setState({username: e.target.value})
}
render() {
return (
<form>
<p>{this.state.username}</p>
<input type="text" value={this.state.username} onChange={this.nameChanged}/>
</form>
)
}
}
|
4.2 非受控表单
表单元素的值由 DOM 元素本身管理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| class App extends Component {
constructor () {
this.onSubmit = this.onSubmit.bind(this)
}
onSubmit(e) {
console.log(this.username.value)
e.preventDefault();
}
render(
<form onSubmit={this.onSubmit}>
<input type="text" ref={username => this.username = username}/>
</form>
)
}
|
5. 路由
url 地址与组件之间的对应关系,访问不同的 url 地址显示不同的组件。
下载:npm install react-router-dom
5.1.1 路由基本使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| // App.js
import React from 'react';
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route, Link } from 'react-router-dom';
function Index() {
return <div>首页</div>;
}
function News() {
return <div>新闻</div>;
}
function App() {
return (
<Router>
<div>
<Link to="/index">首页</Link>
<Link to="/news">新闻</Link>
</div>
<div>
<Route path="/index" component={Index}/>
<Route path="/news" component={News}/>
</div>
</Router>
);
}
|
5.1.2 路由嵌套
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| function News(props) {
return (
<div>
<div>
<Link to={`${props.match.url}/company`}>公司新闻</Link>
<Link to={`${props.match.url}/industry`}>行业新闻</Link>
</div>
<div>
<Route path={`${props.match.path}/company`} component={CompanyNews} />
<Route path={`${props.match.path}/industry`} component={IndustryNews}/>
</div>
</div>
);
}
function CompanyNews() {
return <div>公司新闻</div>
}
function IndustryNews() {
return <div>行业新闻</div>
}
|
5.1.3 路由传参
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| import url from 'url';
class News extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
list: [{
id: 1,
title: '新闻1'
}, {
id: 2,
title: '新闻2'
}]
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>新闻列表组件</div>
<ul>
this.state.list.map((item, index) => {
return (
<li key={index}>
<Link to={`/detail?id=${item.id}`}>{item.title}</Link>
</li>
);
})
</ul>
</div>
);
}
}
class Detail extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
const { query } = url.parse(this.props.location.search, true);
console.log(query); // {id: 1}
render() {
return <div>新闻详情</div>
}
}
|
5.1.4 路由重定向
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| import { Redirect } from 'react-router-dom';
class Login extends Component {
render() {
if (this.state.isLogin) {
return <Redirect to="/"/>
}
}
}
|





